Cortisol is a hormone essential for the stress response, although high cortisol levels can cause weight gain, fatigue and anxiety. Reduce cortisol levels involves practices such as exercise, a balanced diet and relaxation techniques.
Summary
In this article, you will understand the role of cortisol in the body, the symptoms of high cortisol, how to identify them and, most importantly, how balance cortisol levels in a natural and effective way.
Explanatory video on the effects of cortisol:
Cortisol: what it is, what it is for and how it works in the body
THE cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands, located above the kidneys. It is known as the stress hormone, then is released into the bloodstream during situations of physical or emotional stress. The main function of cortisol is to prepare the body to react to stress by mobilizing energy, regulating blood pressure and balancing metabolic and immunological processes.
Essential functions of cortisol
THE cortisol plays an important role in regulating blood sugar levels, helping with the use of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. It also acts in maintaining blood pressure and water and electrolyte balance.
In summary, Cortisol is essential for the healthy functioning of the body, as long as it is maintained at adequate levels.
Impacts of high cortisol
High levels of cortisol for a long time can affect health, leading to sleep problems, weight gain (especially in the abdominal region), high blood pressure and a weakened immune system. increased cortisol in the body is also associated with loss of muscle mass and the development of Cushing's syndrome.
High Cortisol: What Causes It and Why It Happens
High cortisol may be a consequence of emotional and physiological factors. Stressful situations prolonged periods, such as work overload, personal conflicts or chronic anxiety, can lead to excessive production of cortisol by the adrenal glands.

Factors that contribute to elevated cortisol
Factors such as sleep deprivation, excessive caffeine consumption, diet rich in sugar and sedentary lifestyle can increase cortisol production. In addition, hormonal disorders and metabolic diseases are also involved.
Impact of health problems
Medical conditions such as chronic hypertension, Cushing's syndrome and endocrine disorders directly affect the cortisol production. In all cases, it is essential to seek medical advice to carry out a cortisol test and evaluate the most appropriate treatment.
👉 Excess cortisol is just one of the ways in which Hormonal imbalance can affect your physical and emotional health.
Symptoms of high cortisol: how to identify the signs in everyday life
Symptoms of high cortisol can be confused with signs of other conditions, but there are clear indications. Among the main signs and symptoms they are persistent fatigue, abdominal weight gain, insomnia, high blood pressure, anxiety and irritability and difficulty concentrating.
Effects on general well-being
Furthermore, Cortisol can also affect the immune system, leaving the body more vulnerable to infections. Frequent headaches, acne, and digestive problems can also be signs of high cortisol levels.
Being aware of these symptoms allows you to act early and maintain blood cortisol levels under control.
Low Cortisol: What Are the Symptoms and How It Affects Your Health?
Although less spoken, low cortisol is also harmful. When the cortisol levels in the body are too low, the body loses its ability to react adequately to stress.

Symptoms of low cortisol
Among the most common symptoms are intense fatigue, low blood pressure, loss of appetite and involuntary weight gain, hypoglycemia (drop in blood sugar) and dizziness, fainting and muscle weakness.
Symptoms of low cortisol may be indicative of Addison's disease or problems in production of cortisol by the adrenal glands.
How to Control and Reduce Cortisol Naturally
Reduce cortisol levels can be done naturally, with changes in habits. The most recommended practices include regular practice of moderate physical activities, meditation, yoga and breathing techniques, in addition to quality sleep and reduction of caffeine and alcohol.
These habits help balance the cortisol production, improving mood and well-being.
Foods and habits that help reduce cortisol
A healthy diet too can help reduce levels of the “stress hormone”. Foods rich in vitamin C, magnesium and omega-3 have a direct role in modulating the hormone.
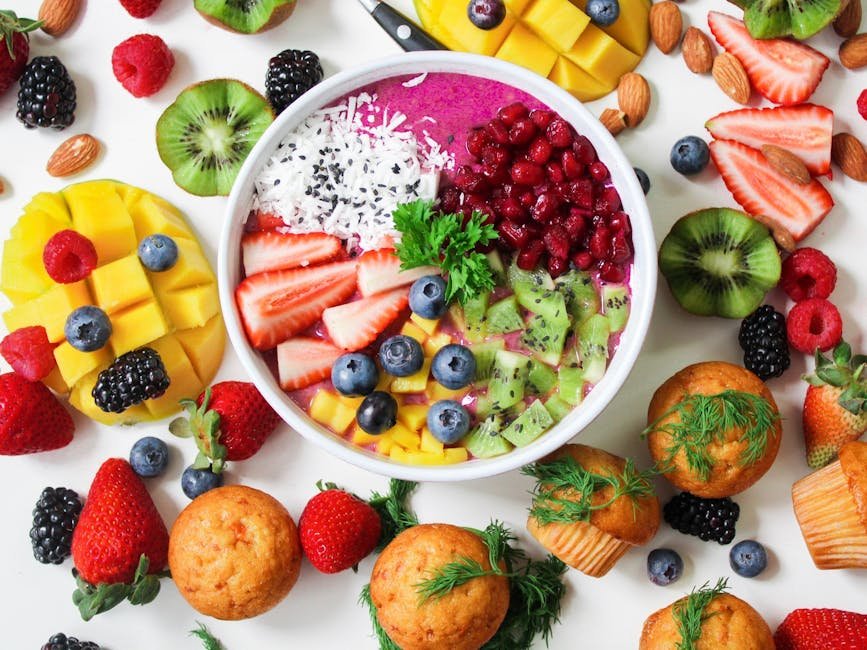

Recommended foods include:
- Citrus fruits (orange, kiwi)
- Dark green leaves (spinach, cabbage)
- Oilseeds (chestnuts, almonds)
- Oily fish (salmon, sardines)
Furthermore, maintain a balanced routine, with breaks, leisure and healthy social interaction, can positively affect stress and cortisol control.
What is basal cortisol and how is it assessed?
Basal cortisol refers to amount of cortisol in the blood measured at rest, usually early in the morning. It represents the baseline of cortisol production in the body and helps diagnose hormonal imbalances.
How is the exam done?
The exam can be done by:
- Blood collection (most common)
- Saliva collection (evaluates variations throughout the day)
- 24-hour urine test
These tests help identify cases of insufficient or excessive production of cortisol, being crucial to detect Cushing's syndrome or Addison's disease.
Cortisol test: types, when to do it and how to interpret it
THE cortisol test is requested when hormonal imbalances are suspected. It helps to understand how the body is dealing with stress and whether there is inadequate hormone production.

Types of exams
- Blood: morning collection
- Saliva: evaluates variations throughout the day
- Urine: measures 24-hour excretion
The interpretation must be made by a doctor, considering the patient's symptoms and history.
Salivary cortisol and blood test: what's the difference?
THE difference between salivary cortisol and blood test is in the type of cortisol assessed. The salivary test measures the free cortisol, active in the body, while the blood test measures total cortisol, including inactive fractions.
Both are important and often used together for a more complete assessment.
Cortisol detox: myth or real solution for stress?
The term "cortisol detox" is used for practices that promise to eliminate excess cortisol in the body. However, the body already has natural regulation mechanisms.

Focus on lifestyle:
- There are no miracle supplements
- Relaxation practices, nutrition and physical activity are more effective
Reduce stress naturally is more sustainable than looking for immediate and unproven solutions.
When to Seek Medical Help for Imbalances
It is important to be aware of signs of imbalance, both for high cortisol as low cortisol. If symptoms such as extreme fatigue, weight changes, insomnia or depression persist, it is essential to seek medical advice.
When to investigate:
- Unexplained weight gain or loss
- Sudden mood swings
- Decreased physical and mental performance
Medical monitoring ensures an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Conclusion: How to keep your hormones balanced for a healthy life
Cortisol is an essential hormone, but excess or deficiency can seriously compromise health. Control the levels of this hormone through healthy habits and paying attention to the body's signals is essential.
Summary of main points
- THE hormone is produced by the adrenal glands;
- High levels of cortisol can cause fatigue, weight gain and anxiety;
- Chronic stress is the main cause of high cortisol;
- It is possible reduce levels naturally with sleep, food and relaxation;
- Blood, saliva and urine tests are used to diagnose imbalances;
- Identify the symptoms and seeking medical help are crucial steps toward well-being.
Take care of your cortisol level is an effective way to promote physical, emotional and mental health.